- admin
- October 11, 2023
- 7:21 am
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), not to be confused with PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disease), is a common hormonal disorder affecting people with ovaries. PCOS is characterized by a range of symptoms and can have various underlying causes. Here’s a demystification of PCOS, including its causes, symptoms, and diagnosis.

Causes Of PCOS:
The exact cause of PCOS is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, hormonal and environmental factors. Key factors include:
- Insulin Resistance: Many individuals with PCOS have insulin resistance, which can lead to elevated insulin levels. High insulin levels may contribute to increased androgen (male hormone) production by the ovaries.
- Hormonal Imbalance: PCOS is associated with an imbalance in sex hormones, particularly increased levels of androgens (e.g. testosterone) and irregularities in the menstrual cycle.
- Genetics: There is a genetic component and PCOS often runs in families.
- Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation may play a role in the development of PCOS.

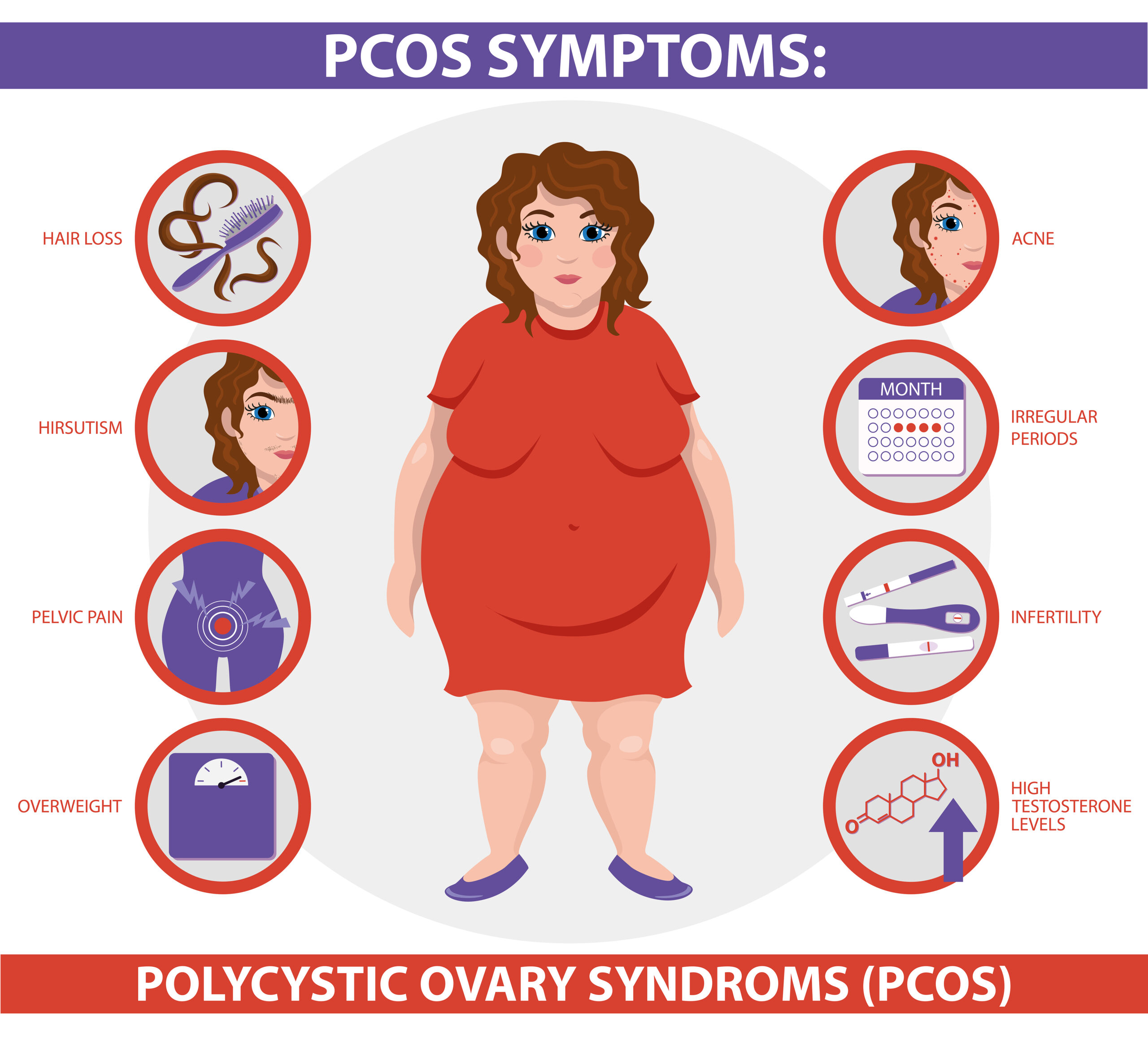
Symptoms Of PCOS:
PCOS presents with a wide range of symptoms that can vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
- Irregular Menstrual Periods: Irregular, infrequent or absent menstrual periods are a hallmark of PCOS.
- Ovulation Issues: PCOS can lead to anovulation (lack of ovulation), making it challenging to conceive.
- Hyperandrogenism: Elevated androgen levels can cause symptoms such as acne, hirsutism (excessive hair growth) and male-pattern baldness.
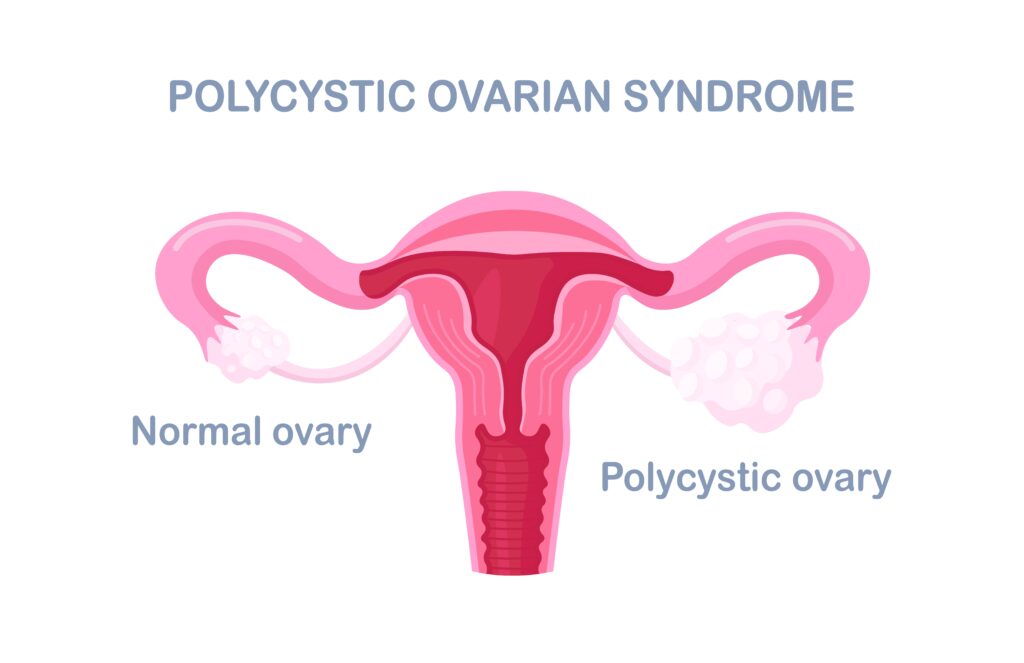
- Polycystic Ovaries: On ultrasound, the ovaries may appear enlarged and contain multiple small cysts (follicles).
- Weight Gain: Many individuals with PCOS experience weight gain or have difficulty losing weight.
- Skin Changes: Skin problems like acne and skin tags may occur.
- Mood Disturbances: PCOS can be associated with mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety.
Diagnosis Of PCOS:
The diagnosis of PCOS is typically made based on a combination of clinical symptoms, physical examination and specific criteria. To diagnose PCOS, healthcare providers typically consider the following:
- Menstrual History: Irregular periods or a lack of menstruation is a common indicator.
- Physical Examination: Signs of hyperandrogenism, such as acne or excess hair growth, may be observed.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests to measure hormone levels, including testosterone, LH (luteinizing hormone), FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and insulin, are performed.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the pelvis can reveal the presence of polycystic ovaries.
- To receive a diagnosis of PCOS, other possible conditions with similar symptoms, such as thyroid disorders and hyperprolactinemia, should be ruled out.
It’s important to note that PCOS is a complex condition and not all individuals will experience the same symptoms or severity. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial as PCOS is associated with potential long-term health risks, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and fertility issues. Treatment is often tailored to address specific symptoms and may include lifestyle modifications, hormonal therapy, and other interventions as needed.